【第35回】AWS CloudFormationを用いた基盤自動化(15)SpringCloudAWSを利用したFrontend Webアプリケーションにおけるスタック情報の取得・設定¶
本連載では、以下のイメージの構成にあるAWSリソース基盤自動化環境の構築を実践しています。
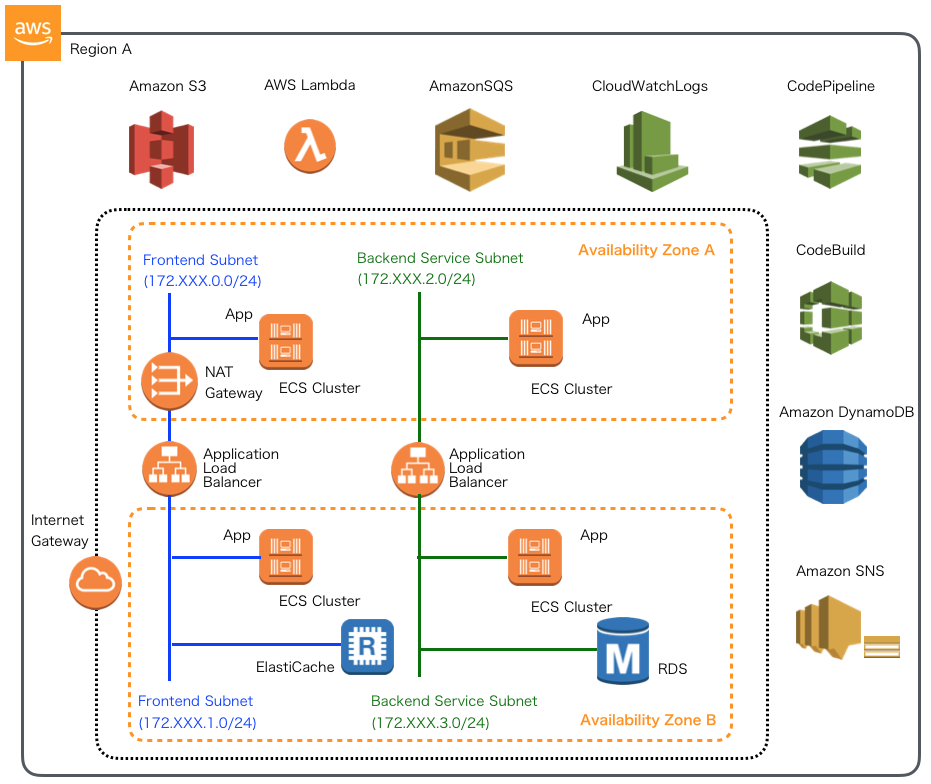
前回は、RDS、DynamoDB、SQSからのキュー取得を行う、Backend Serviceアプリケーションで、Spring Cloud AWSを用いて、CloudFormationを使ってスタック情報を取得し、アプリケーションの設定を行いました。 引き続き今回は、ALB、ElastiCache、S3といったリソースアクセス、SQSへのキュー送信を行うFrontend Webアプリケーションにおいて、Spring Cloud AWSを用いて取得したスタック情報を使ったアプリケーションの設定実装を紹介します。 実際のソースコードは GitHub 上にコミットしています。 ソースコード中で本質的でない記述を一部省略しているので、実行コードを作成する場合は、必要に応じて適宜GitHub上のソースコードも参照してください。
Frontend WebアプリケーションにおけるCloudFormationスタック情報を利用した設定¶
まず、Mavenプロジェクトのpom.xmlで、spring-boot-starter-web、spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf、spring-cloud-starter-awsのライブラリを定義します。 また、ElastiCache(Redis)へアクセスするためにはspring-session-data-redis、AWS ElastiCacheのSDKのライブラリおよびRedisのドライバとなるletteceを、SQSのアクセスにはspring-cloud-starter-aws-messagingを合わせて追加する必要があります。
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-aws</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.session</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-session-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.amazonaws</groupId>
<artifactId>aws-java-sdk-elasticache</artifactId>
<version>1.11.415</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.lettuce</groupId>
<artifactId>lettuce-core</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-aws-messaging</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Frontend Webアプリケーションでは以下のような設定クラスの構成で実装します。これまでの連載で実装した内容から差分があるものを中心に解説します。
注釈
アプリケーションではALBやElastiCache、S3へアクセスする実装、SQSへキュー送信する実装クラスなどもありますが、これまでの連載で踏襲した実装にしているのでここでは詳しい解説は行いません。 詳細な説明は クラウドネイティブ第6回 や 第20回 、 第26回 、第29回 を参照してください。
| コンポーネント | 説明 | 必須 |
| WebApp | SpringBootアプリケーションを実行する起動クラス。以前の連載と設定は変わらないため説明は省略。 | ◯ |
| DomainConfig | サービスレイヤの設定を行うクラス。以前の連載と設定は変わらないため説明は省略。 | |
| RedisConfig | ElastiCache(Redis)に関する設定クラス。 | ◯ |
| S3Config | S3に関する設定クラス。 | ◯ |
| MvcConfig | Webサービスに関する設定クラス。以前の連載と設定は変わらないため説明は省略。 | ◯ |
| DevConfig | 開発環境に依存する内容の設定クラス。ElastiCache、S3、SQSで定義が必要なもので開発環境に依存する部分を切り出して設定する。 | ◯ |
| StagingConfig | ステージング環境に依存する内容の設定クラス。ElastiCache、S3、SQSで定義が必要なものでステージング環境に依存する部分を切り出して設定する。 | ◯ |
| ProductionConfig | 商用環境に依存する内容の設定クラス。ElastiCache、S3、SQSで定義が必要なもので商用環境に依存する部分を切り出して設定する。ステージング環境とほぼ同等となる(本来プロダクションの設定がステージングで動くようにするのがあるべき設定)のため、説明は省略する。 | ◯ |
設定のポイントを先に述べますが、ElastiCacheの設定としては、LettuceConnectionFactoryにCloudFormationClient経由でスタック情報から取得したエンドポイントとポートを指定します。 S3においては特別な設定は不要になりますが、アクセス対象となるバケットをスタック情報から取得します。SQSにおいては、事前にQueueMessagingTemplateにスタック情報から、キューのサービスエンドポイントとリージョンおよび 送信先のキュー名を取得して設定するかたちになります。目指す実装のあり方としては、環境ごとにプロファイルを切り替えるだけで、各環境ごとにアプリケーションが同じように動くようにすることです。それでは順次アプリケーションの設定実装をみていきましょう。
まず、ElastiCacheの設定クラスを行うRedisConfigですが、第20回 で解説したときと同じく、 Redis内に保存したデータを確認するための設定のみを行います。
package org.debugroom.mynavi.sample.cloudformation.frontend.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializer;
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
@Bean
public RedisSerializer<Object> springSessionDefaultRedisSerializer() {
return new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer();
}
}
なお、以前の連載の実装では、「ConfigureRedisAction」を「NO_OP」とする設定(ElastiCacheではconfigコマンドの実行が禁止されているため)を定義し、RedisのホストURLやポートをapplication.ymlで環境変数で指定するかたちをとっていましたが、 今回、環境に依存する設定はDevConfigへ移管し、CloudFormationのスタック情報経由で取得します。説明は後述します。
続いて、S3の設定を行うS3Configですが、第26回 同様、AmazonSDKから提供されているS3クライアントであるcom.amazonaws.services.s3.AmazonS3のみを定義すれば問題ありません。
package org.debugroom.mynavi.sample.cloudformation.frontend.config;
import com.amazonaws.services.s3.AmazonS3;
import com.amazonaws.services.s3.AmazonS3ClientBuilder;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class S3Config {
@Bean
public AmazonS3 amazonS3(){
return AmazonS3ClientBuilder.standard().build();
}
}
また、FrontendのWebアプリケーションでも、Backendのアプリケーションと連携を想定して、キュー送信の処理を実装していますが、SQSの設定は、環境依存のパラメータを使った設定のみになりますので、特に共通のSQS設定クラスは作成しません。
注釈
アプリケーション内でのS3アクセスはバケット名が必要なので、下記の実装例のように、CloudFormationのスタック情報から取得することを想定したS3バケット名を保持するコンポーネントを作成します(バケット名を設定する実装例は後述)。
package org.debugroom.mynavi.sample.cloudformation.common.apinfra.cloud.aws;
// omit
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@Builder
@Data
public class S3Info {
private String bucketName;
}
S3へアクセスしたいアプリケーションの処理は クラウドネイティブ第27回 で解説した実装と同様ですが、@Autowiredでインジェクションした上記のコンポーネントから取得したバケット名を、SpringのResourceLoaderを使ってオブジェクトキーと合わせて指定すればアクセスが可能です。
package org.debugroom.mynavi.sample.cloudformation.frontend.app.web.helper;
// omit
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;
import org.springframework.core.io.ResourceLoader;
import org.springframework.core.io.WritableResource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.debugroom.mynavi.sample.cloudformation.common.apinfra.cloud.aws.S3Info;
@Component
public class S3DownloadHelper{
private static final String S3_BUCKET_PREFIX = "s3://";
private static final String DIRECTORY_DELIMITER = "/";
@Autowired
S3Info s3Info;
@Autowired
ResourceLoader resourceLoader;
@Value("classpath:sample.jpg")
Resource imageResource;
public BufferedImage getImage(String imageFilePath){
Resource resource = resourceLoader.getResource(
new StringBuilder()
.append(S3_BUCKET_PREFIX)
.append(s3Info.getBucketName())
.append(DIRECTORY_DELIMITER)
.append(imageFilePath)
.toString());
BufferedImage image = null;
try(InputStream inputStream = resource.getInputStream()){
image = ImageIO.read(inputStream);
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return image;
}
// omit
同様に、アプリケーションから参照することを目的としたSQSのキュー名を取得するコンポーネントクラスも実装しておきます。
package org.debugroom.mynavi.sample.cloudformation.common.apinfra.cloud.aws;
// omit
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@Builder
@Data
public class SQSInfo {
private String queueName;
}
アプリケーションのキューの送信処理は クラウドネイティブ第29回 と同様、SQSのキュー名を指定し、queueMessagingTemplate#convertAndSend()メソッドを実行すればOKです。
package org.debugroom.mynavi.sample.cloudformation.frontend.domain.repository.async;
import org.debugroom.mynavi.sample.cloudformation.common.apinfra.cloud.aws.SQSInfo;
// omit
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cloud.aws.messaging.core.QueueMessagingTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class SampleRepositoryImpl implements SampleRepository{
@Autowired
SQSInfo sqsInfo;
@Autowired
QueueMessagingTemplate queueMessagingTemplate;
@Override
public void save(Sample sample) {
queueMessagingTemplate.convertAndSend(sqsInfo.getQueueName(),
sample.getSampleText());
}
警告
Spring Cloud AWS の2020年1月時点の最新バージョン2.2.1 RELEASEでは、ResourceLoaderによるS3書き込みアクセスがエラーとなります。 Resourceを検索するデフォルトのリゾルバにS3が追加されなくなったためで、WritableResourceを使ってファイルのアップロードを行おうとすると、Caused by: java.lang.ClassCastException: org.springframework.web.context.support.ServletContextResource cannot be cast to org.springframework.core.io.WritableResource が発生します。 これを回避するには、SimpleStorageProtocolResolverにAmazonS3クライアントを加えて、オブジェクトキーを取得して下さい。また、TaskExecutorが設定されておらず、Caused by: java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: TaskExecutor must not be null が発生する場合はSyncTaskExecutorをセットしましょう。
Resource newResource = resourceLoader.getResource(objectKey);
if(!newResource.getClass().getName().endsWith("SimpleStorageResource")
&& resourceLoader instanceof DefaultResourceLoader){
SimpleStorageProtocolResolver simpleStorageProtocolResolver = new SimpleStorageProtocolResolver(amazonS3);
simpleStorageProtocolResolver.setTaskExecutor(new SyncTaskExecutor());
newResource = simpleStorageProtocolResolver.resolve(objectKey, resourceLoader);
}
WritableResource writableResource = (WritableResource)newResource;
try(InputStream inputStream = imageResource.getInputStream();
OutputStream outputStream = writableResource.getOutputStream()){
IOUtils.copy(inputStream, outputStream);
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
そして、開発環境向けのの設定を行うDevConfigクラスを実装します。ここでは、CloudFormationで構築したスタックの情報を取得し、開発環境固有となる設定を行います。今回サンプルとして実装した例は以下の通りです。
package org.debugroom.mynavi.sample.cloudformation.frontend.config;
import com.amazonaws.client.builder.AwsClientBuilder;
import com.amazonaws.services.sqs.AmazonSQSAsync;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.web.client.RestTemplateBuilder;
import org.springframework.cloud.aws.context.config.annotation.EnableStackConfiguration;
import org.springframework.cloud.aws.messaging.core.QueueMessagingTemplate;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Profile;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.lettuce.LettuceConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.session.data.redis.config.ConfigureRedisAction;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestOperations;
import org.debugroom.mynavi.sample.cloudformation.common.apinfra.cloud.aws.S3Info;
import org.debugroom.mynavi.sample.cloudformation.common.apinfra.cloud.aws.SQSInfo;
import org.debugroom.mynavi.sample.cloudformation.common.apinfra.cloud.aws.CloudFormationStackInfo;
import org.debugroom.mynavi.sample.cloudformation.common.apinfra.log.interceptor.MDCLoggingInterceptor;
@Profile("dev") // …(A)
@EnableStackConfiguration(stackName = "mynavi-sample-infra-dev") // …(B)
@Configuration
public class DevConfig {
private static final String BACKEND_SERVICE_DNS = "http://localhost:8080"; // …(C)
private static final String S3_STACK_NAME = "S3DevStack";
private static final String S3_BUCKET_EXPORT = "MynaviSampleS3Bucket-Dev"; // …(D)
private static final String SQS_STACK_NAME = "SQSDevStack";
private static final String SQS_QUEUE_EXPORT = "MynaviSampleSQS-Dev";
private static final String SQS_ENDPOINT_EXPORT = "MynaviSampleSQS-Dev-ServiceEndpoint"; // …(E)
private static final String SQS_REGION_EXPORT = "MynaviSampleSQS-Dev-Region";
private static final String ELASTICACHE_STACK_NAME = "ElastiCacheDevStack"; // …(F)
private static final String ELASTICACHE_ENDPOINT_EXPORT = "mynavi-sample-cloudformation-vpc-ElastiCacheRedisEndPoint-Dev";
private static final String ELASTICACHE_PORT_EXPORT = "mynavi-sample-cloudformation-vpc-ElastiCacheRedisPort-Dev";
@Bean
public RestOperations restOperations(RestTemplateBuilder restTemplateBuilder){ // …(G)
return restTemplateBuilder.rootUri(BACKEND_SERVICE_DNS)
.interceptors(new MDCLoggingInterceptor()).build();
}
@Bean
CloudFormationStackInfo cloudFormationStackInfo(){ // …(H)
return new CloudFormationStackInfo();
}
@Bean
S3Info s3Info(){ // …(I)
return S3Info.builder()
.bucketName(cloudFormationStackInfo()
.getExportValue(S3_STACK_NAME, S3_BUCKET_EXPORT))
.build();
}
@Bean
SQSInfo sqsInfo(){ // …(J)
return SQSInfo.builder()
.queueName(cloudFormationStackInfo().getExportValue(
SQS_STACK_NAME, SQS_QUEUE_EXPORT))
.build();
}
@Autowired
AmazonSQSAsync amazonSQSAsync; // …(K)
@Bean
public AwsClientBuilder.EndpointConfiguration endpointConfiguration(){ // …(L)
return new AwsClientBuilder.EndpointConfiguration(
cloudFormationStackInfo().getExportValue(
SQS_STACK_NAME, SQS_ENDPOINT_EXPORT),
cloudFormationStackInfo().getExportValue(
SQS_STACK_NAME, SQS_REGION_EXPORT));
}
@Bean
public QueueMessagingTemplate queueMessagingTemplate(){ // …(M)
return new QueueMessagingTemplate(amazonSQSAsync);
}
/*
* ElasitiCache is not permitted public access, use local redis server except dev environment in vpc.
*/
@Bean
public ConfigureRedisAction configureRedisAction() { // …(N)
return ConfigureRedisAction.NO_OP;
}
@Bean
public LettuceConnectionFactory lettuceConnectionFactory(){ // …(O)
return new LettuceConnectionFactory(
cloudFormationStackInfo().getExportValue(
ELASTICACHE_STACK_NAME, ELASTICACHE_ENDPOINT_EXPORT),
Integer.valueOf(cloudFormationStackInfo().getExportValue(
ELASTICACHE_STACK_NAME, ELASTICACHE_PORT_EXPORT)));
}
}
DevConfig設定クラスの実装のポイントは(A)〜(O)の通りです。
| 記述 | 説明 |
| Springの起動時にプロファイル"dev"が指定されたときに有効化されるよう@Profileアノテーションを設定します。 | |
| @EnableStackConfigurationのstackName属性に、 NestedStackの作成 でNestedStackとして作成したスタック名を指定します。この設定により指定したスタックに定義されたリソースにおける、SpringCloudAWSがサポートする自動設定が可能になります。 | |
| 可読性向上のために、Backend Serviceアプリケーションを呼び出す場合RestTemplateに設定するALBのDNSを定数値として定義します。 | |
| 可読性向上のために、S3を構築するCloudFormationテンプレートで定義した開発用のスタック名やエクスポート名を定数値として定義します。 | |
| 可読性向上のために、SQSを構築するCloudFormationテンプレートで定義した開発用のスタック名やエクスポート名を定数値として定義します。 | |
| 可読性向上のために、ElastiCacheを構築するCloudFormationテンプレートで定義した開発用のスタック名やエクスポート名を定数値として定義します。 | |
| (C)で定義したALBのDNS名を用いてRestTemplate(インターフェースはRestOperations)のBean定義を行います。 | |
| Backend ServiceにおけるCloudFormationスタック情報を利用した設定 と同様、AmazonCloudFormationClientからスタック情報を取得する共通のユーティリティクラスをBean定義します。 | |
| (H)のユーティリティクラスから、(D)で定義した定数値を使って、S3のバケット名を取得し設定します。 | |
| (H)のユーティリティクラスから、(D)で定義した定数値を使って、SQSのキュー名を取得し設定します。 | |
| spring-cloud-starter-aws-messagingをpom.xmlで依存性定義することで追加されるAmazonSQSクライアントをインジェクションします。 | |
| (H)のユーティリティクラスから、(E)で定義した定数値を用いて、SQSのエンドポイントを定義します。 | |
| (K)におけるSQSクライアントのBean定義を使って、QueueMessagingTemplateをBean定義します。 | |
| ElastiCacheではconfigコマンドの実行が禁止されているため、ConfigureRedisActionを「NO_OP」に設定します。 | |
| (H)のユーティリティクラスから、(F)で定義した定数値を用いて、RedisConnectionFactoryを継承したLettuceConnectionFactoryをBean定義します。 |
続いて、ステージング(プロダクションも同等)環境固有の設定を行うStagingConfigの実装サンプルは以下の通りです。定数値以外、クラスの構成はほぼ開発環境と同等ですので詳細な説明は割愛します。 主な差分はALBのエンドポイントはスタック情報から取得する実装に変わったところです。
package org.debugroom.mynavi.sample.cloudformation.frontend.config;
// omit
@Profile("staging")
@EnableStackConfiguration(stackName = "mynavi-sample-infra-staging")
@Configuration
public class StagingConfig {
private static final String PROTOCOL = "http://";
private static final String ALB_STACK_NAME = "ALBStagingStack";
private static final String ALB_BACKEND_ALB_EXPORT_NAME = "mynavi-sample-cloudformation-vpc-BackendALBDNS-Staging";
private static final String S3_STACK_NAME = "S3StagingStack";
private static final String S3_BUCKET_EXPORT = "MynaviSampleS3Bucket-Staging";
private static final String SQS_STACK_NAME = "SQSStagingStack";
private static final String SQS_QUEUE_EXPORT = "MynaviSampleSQS-Staging";
private static final String SQS_ENDPOINT_EXPORT = "MynaviSampleSQS-Staging-ServiceEndpoint";
private static final String SQS_REGION_EXPORT = "MynaviSampleSQS-Staging-Region";
private static final String ELASTICACHE_STACK_NAME = "ElastiCacheStagingStack";
private static final String ELASTICACHE_ENDPOINT_EXPORT = "mynavi-sample-cloudformation-vpc-ElastiCacheRedisEndPoint-Staging";
private static final String ELASTICACHE_PORT_EXPORT = "mynavi-sample-cloudformation-vpc-ElastiCacheRedisPort-Staging";
@Bean
CloudFormationStackInfo cloudFormationStackInfo(){
return new CloudFormationStackInfo();
}
@Bean
public RestOperations restOperations(RestTemplateBuilder restTemplateBuilder){
return restTemplateBuilder.rootUri(PROTOCOL + cloudFormationStackInfo().getExportValue(
ALB_STACK_NAME , ALB_BACKEND_ALB_EXPORT_NAME))
.interceptors(new MDCLoggingInterceptor()).build();
}
@Bean
S3Info s3Info(){
return S3Info.builder()
.bucketName(cloudFormationStackInfo()
.getExportValue(S3_STACK_NAME, S3_BUCKET_EXPORT))
.build();
}
@Bean
SQSInfo sqsInfo(){
return SQSInfo.builder()
.queueName(cloudFormationStackInfo().getExportValue(
SQS_STACK_NAME, SQS_QUEUE_EXPORT))
.build();
}
@Autowired
AmazonSQSAsync amazonSQSAsync;
@Bean
public AwsClientBuilder.EndpointConfiguration endpointConfiguration(){
return new AwsClientBuilder.EndpointConfiguration(
cloudFormationStackInfo().getExportValue(
SQS_STACK_NAME, SQS_ENDPOINT_EXPORT),
cloudFormationStackInfo().getExportValue(
SQS_STACK_NAME, SQS_REGION_EXPORT));
}
@Bean
public QueueMessagingTemplate queueMessagingTemplate(){
return new QueueMessagingTemplate(amazonSQSAsync);
}
@Bean
public ConfigureRedisAction configureRedisAction() {
return ConfigureRedisAction.NO_OP;
}
@Bean
public LettuceConnectionFactory lettuceConnectionFactory(){
return new LettuceConnectionFactory(
cloudFormationStackInfo().getExportValue(
ELASTICACHE_STACK_NAME, ELASTICACHE_ENDPOINT_EXPORT),
Integer.valueOf(cloudFormationStackInfo().getExportValue(
ELASTICACHE_STACK_NAME, ELASTICACHE_PORT_EXPORT)));
}
注釈
Spring Cloud AWSには@EnableElastiCacheを使ったElastiCacheの自動設定サポートがありますが、用途としてキャッシュが想定されていて、今回のユースケースのように複数のコンテナアプリケーションからセッション共有することを目的としたサポートではありません。 Springのセッション共有のスタンダードなサポートでは、Mavenで定義した通り、spring-session-data-redisを使用するからです。spring-session-data-redisの使用方法に則り、LettuceConnectionFactoryでスタンドアローンモードでElastiCacheのエンドポイントとポートを指定するようにしましょう。 ちなみにセッション共有とキャッシュでは、可用性などの非機能要件が異なるので(キャッシュはなくても動作することが望ましいですが、共有領域にセッションデータが保存できないとアプリケーションとしては致命的です)、複数のElastiCacheを構築して、用途に応じてを使い分けるようにしてください。
前回のBackend Serviceアプリケーションに引き続き、今回はFrontend WebアプリケーションでCloudFormationのスタック情報を用いて、ElastiCacheやS3、SQSキュー送信の設定情報を取得する実装方法を紹介しました。 アプリケーションで各環境ごとに変わるパラメータを環境変数として参照する実装は分かりやすくて良いのですが、環境変数の数が多くなってくると管理も大変になります。 CloudFormationを使って基盤情報を構築するのであれば、環境変数を用いずとも、このようにスタック情報から各環境ごとに変わるパラメータを取得する実装が可能になります。
次回は構築したアプリケーションのコンテナイメージを作成し、ECSクラスタ定義、タスク定義、サービス構築をCloudFormationテンプレートを使って実装します。
著者紹介¶
川畑 光平(KAWABATA Kohei) - NTTデータ 課長代理

金融機関システム業務アプリケーション開発・システム基盤担当を経て、現在はソフトウェア開発自動化関連の研究開発・推進に従事。
Red Hat Certified Engineer、Pivotal Certified Spring Professional、AWS Certified Solutions Architect Professional等の資格を持ち、アプリケーション基盤・クラウドなど様々な開発プロジェクト支援にも携わる。