【第10回】AWS X-Rayを用いたマイクロサービスの可視化(3)¶
本連載では、以下に示すようなマイクロサービスアーキテクチャのアプリケーション環境を構築しています。
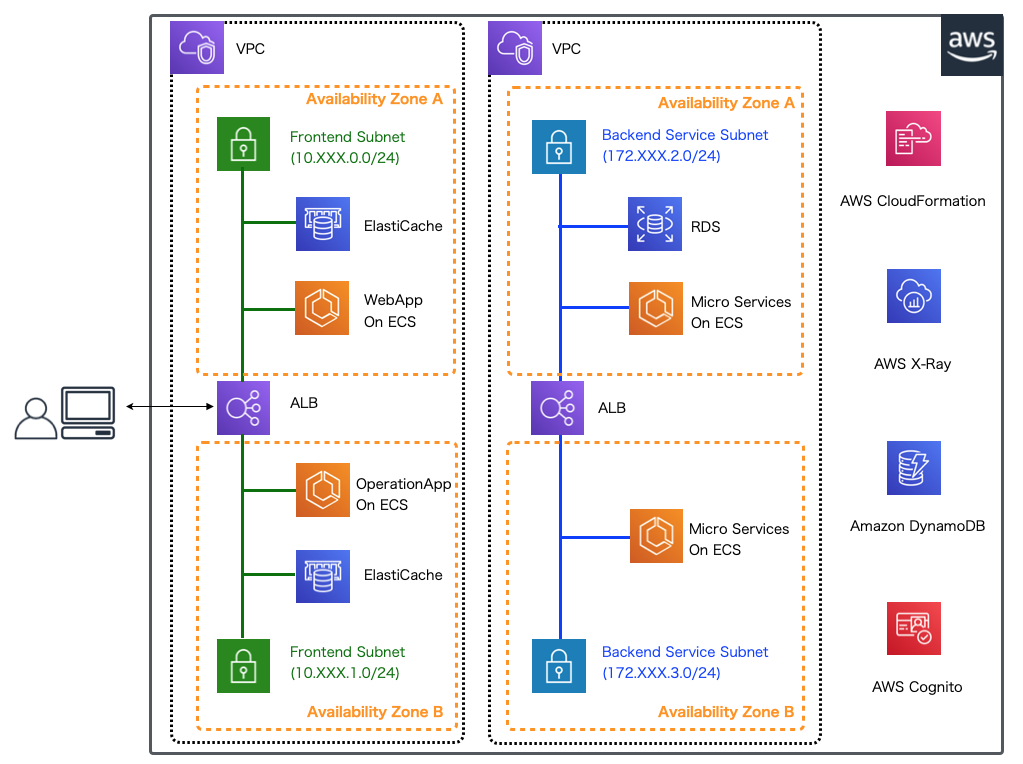
前回はAWS X-Rayのセグメント・サブセグメントの概念を解説し、フロントエンドのWebアプリケーション、バックエンドのマイクロサービス双方に共通する設定の実装を行いました。 今回はX-Rayデーモンへトレースデータを送信するためのフロントエンドのWebアプリケーションの設定の個別の実装を解説していきます。 本連載で実際に作成するアプリケーションでは GitHub 上にコミットしています。 以降に記載するソースコードでは、import文など本質的でない記述を省略している部分があるので、実行コードを作成する際は、必要に応じて適宜GitHubにあるソースコードも参照してください。
サンプリングルールの設定¶
X-Rayのトレースデータを送信は、指定されたサンプリングルールに基づきデータが送信されます。このアプリケーションでは 前回も解説した通り、共通のX-Rayの設定クラスで、クラスパス配下にある、サンプリングルールを設定したsampling-rules.jsonを読み込んでいます。
package org.debugroom.mynavi.sample.aws.microservice.frontend.webapp.config;
// omit
@Aspect
@Configuration
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
public class XRayConfig extends AbstractXRayInterceptor {
//omit
static {
try{
AWSXRayRecorderBuilder builder = AWSXRayRecorderBuilder.standard()
.withSamplingStrategy(new LocalizedSamplingStrategy(
ResourceUtils.getURL("classpath:sampling-rules.json")));
AWSXRay.setGlobalRecorder(builder.build());
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// omit
@Override
@Pointcut("@within(com.amazonaws.xray.spring.aop.XRayEnabled) " +
" && execution(* org.debugroom.mynavi.sample.aws.microservice..*.*(..))" )
protected void xrayEnabledClasses() {
}
}
サンプリングルールは商用環境などでのリクエスト量のパフォーマンス計測や開発のデバッグを目的とした計測などによって適切なレートは異なります。 ここでは、全てのリクエストが計測対象となるよう、レートを1に設定しておきます。サンプリングルールは対象のホストやHTTPメソッド、URLパスなど細かい設定が可能です。 詳細は サンプリングルールの設定 を参照してください。
{
"version": 2,
"rules": [
{
"description": "Sample description.",
"host": "*",
"http_method": "*",
"url_path": "/api/*",
"fixed_target": 1,
"rate": 1
}
],
"default": {
"fixed_target": 1,
"rate": 0.1
}
}
フロントエンドのWebアプリケーションにおけるX-Rayの設定¶
今回は計測するサブセグメントとして、Controller、Service、Repositoryごとに実行時間を計測します(Spring Securityで認証の際に利用されるCustomUserDetailsも含めています)。 前回設定したXRayConfigクラスのAOPポイントカット定義に基づき、各コンポーネントの実装クラスに@XRayEnabledアノテーションを付与します。下記はControllerにアノテーションを付与する例です。
package org.debugroom.mynavi.sample.aws.microservice.frontend.webapp.app.web;
// omit
import com.amazonaws.xray.spring.aop.XRayEnabled;
// omit
@XRayEnabled
@Controller
public class SampleController {
// omit
}
Repositoryクラスではバックエンドのマイクロサービスを呼び出す処理を実装していましたが、同一のTraceIDが持ち回られるように、リクエストヘッダに指定されたフォーマットでTraceIDを設定しておく必要があります。 X-Ray SDK for JavaではデフォルトでApache HttpComponentsを使ってTraceIDをリクエストヘッダに埋め込んで送信するcom.amazonaws.xray.proxies.apache.http.DefaultHttpClientが提供されていますが、 これまでの連載でHTTPリクエストの送信は、Spring WebFluxが提供するWebClientを使ってバックエンドのサービスを呼び出す処理を実装していたので、aws-xray-recorder-sdk-apache-httpのライブラリを参考に WebClientでTraceIDをリクエストヘッダに共通的に設定する実装を行います。設定クラスの実装は以下の通りです。
package org.debugroom.mynavi.sample.aws.microservice.frontend.webapp.config;
// omit
import com.amazonaws.xray.AWSXRay;
import com.amazonaws.xray.entities.Segment;
import com.amazonaws.xray.entities.Subsegment;
import com.amazonaws.xray.entities.TraceHeader;
import org.springframework.web.reactive.function.client.ClientRequest;
import org.springframework.web.reactive.function.client.ExchangeFilterFunction;
import org.springframework.web.reactive.function.client.WebClient;
// omit
@Configuration
public class DevConfig {
@Autowired
ServiceProperties serviceProperties; //(A)
@Bean
public WebClient userWebClient(){
return WebClient.builder()
.baseUrl(serviceProperties.getDns())
.filter(exchangeFilterFunction()) //(B)
.build();
}
private ExchangeFilterFunction exchangeFilterFunction(){ //(C)
return (clientRequest, nextFilter) -> {
Segment segment = AWSXRay.getCurrentSegment(); //(D)
Subsegment subsegment = AWSXRay.getCurrentSubsegment(); //(E)
TraceHeader traceHeader = new TraceHeader(segment.getTraceId(),
segment.isSampled() ? subsegment.getId() : null,
segment.isSampled() ? TraceHeader.SampleDecision.SAMPLED : TraceHeader.SampleDecision.NOT_SAMPLED);
//(F)
ClientRequest newClientRequest = ClientRequest.from(clientRequest)
.header(TraceHeader.HEADER_KEY, traceHeader.toString())
.build(); //(G)
return nextFilter.exchange(newClientRequest);
};
}
// omit
DevConfigクラスコードの説明は以下の通りです。
| 項番 | 説明 |
| バックエンドのマイクロサービスが実行されているホストのURLを定義したプロパティファイルの値を保持するオブジェクトをインジェクションします。 | |
| WebClientに共通して行うフィルタ処理を定義します。実際の処理は(C)のメソッド内で行います。 | |
| フィルタ処理をorg.springframework.web.reactive.function.client.ExchangeFilterFunctionとして実装します。 | |
| com.amazonaws.xray.AWSXRayから実行中のセグメントオブジェクトを取得します。クラス変数から取得していますが、内部的な実際の処理はスレッドローカルに保存されたオブジェクトを取得しており、スレッドごとに異なるオブジェクトが得られます。 | |
| com.amazonaws.xray.AWSXRayから実行中のサブセグメントオブジェクトを取得します。クラス変数から取得していますが、内部的な実際の処理はスレッドローカルに保存されたオブジェクトを取得しており、スレッドごとに異なるオブジェクトが得られます。 | |
| com.amazonaws.xray.entities.TraceHeaderのインスタンスを(D)、(E)の情報から生成します。なお、これらの実装は TracedHttpClient を参考にしています。 | |
| リクエストヘッダを設定した新しいリクエストを生成して、返却します。 |
また、Controllerの処理が完了した後、TraceIDやユーザID、実行時間をDynamoDBに保存するよう、HanderInterceptorAdapterを継承したコンポーネントを生成します。このクラスはControllerが実行された後に、オーバーライドされたメソッドが常に実行されるようInterceptorとして追加します。 オーバーライドされたメソッド内では、以前の回で実装したものと同様、Spring SecurityのSecurityContextからCustomUserDetailsを取得してユーザIDを設定します。TraceIDは上記の実装と同様Segmentオブジェクトをcom.amazonaws.xray.AWSXRayから取得し、 前回実装したLogクラスに設定してDynamoDBへ保存します。
package org.debugroom.mynavi.sample.aws.microservice.frontend.webapp.app.web.interceptor;
// omit
import com.amazonaws.xray.AWSXRay;
import com.amazonaws.xray.entities.Segment;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;
import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContext;
import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContextHolder;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.HandlerInterceptorAdapter;
import org.debugroom.mynavi.sample.aws.microservice.common.apinfra.cloud.aws.log.dynamodb.model.Log;
import org.debugroom.mynavi.sample.aws.microservice.common.apinfra.cloud.aws.log.dynamodb.repository.LogRepository;
import org.debugroom.mynavi.sample.aws.microservice.common.apinfra.util.DateStringUtil;
import org.debugroom.mynavi.sample.aws.microservice.frontend.webapp.app.web.security.CustomUserDetails;
@Component
public class AuditLoggingInterceptor extends HandlerInterceptorAdapter {
@Autowired(required = false)
LogRepository logRepository;
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
String userId = "0";
SecurityContext securityContext = SecurityContextHolder.getContext();
Authentication authentication = securityContext.getAuthentication();
if(Objects.nonNull(authentication)){
Object principal = authentication.getPrincipal();
if(principal instanceof CustomUserDetails){
userId = ((CustomUserDetails)principal)
.getUserResource().getUserId();
}
}
Log log = Log.builder()
.userId(userId)
.createdAt(DateStringUtil.now())
.traceId(getTraceId())
.build();
logRepository.save(log);
}
private String getTraceId(){
Optional<Segment> segment = AWSXRay.getCurrentSegmentOptional();
if (segment.isPresent()){
return segment.get().getTraceId().toString();
}
return null;
}
}
今回はフロントエンドのWebアプリケーション個別の設定を解説しました。次回はバックエンドのマイクロサービスに必要なAWS X-Rayの個別設定について解説を進めていきます。
著者紹介¶
川畑 光平(KAWABATA Kohei) - NTTデータ

金融機関システム業務アプリケーション開発・システム基盤担当、ソフトウェア開発自動化関連の研究開発を経て、デジタル技術関連の研究開発・推進に従事。
Red Hat Certified Engineer、Pivotal Certified Spring Professional、AWS Certified Solutions Architect Professional等の資格を持ち、アプリケーション基盤・クラウドなど様々な開発プロジェクト支援にも携わる。
AWS Top Engineers & Ambassadors 選出。
本連載記事の内容に対するご意見・ご質問は Facebook まで。